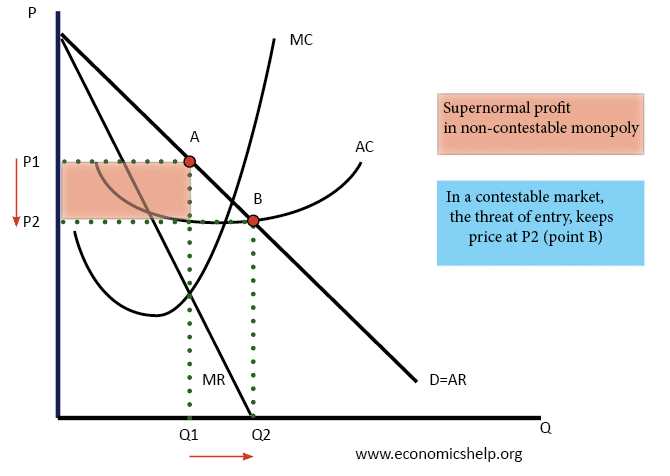
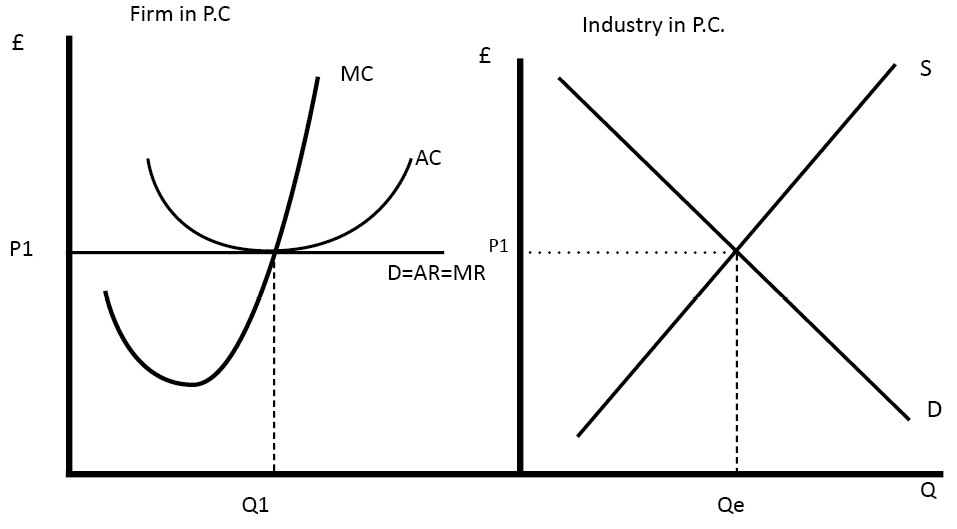
Bertrand Competition
Definition of Bertrand Competition A market structure where it is assumed that there are two firms, who both assume the other firm will keep prices unchanged. Therefore, each firm has an incentive to cut prices, but this actually leads to a price war. If products are perfect substitutes this assumes the price will be driven …